The HIMSS Healthcare Cybersecurity Survey found that across the board, healthcare organizations identified phishing and ransomware attacks as the most significant security incidents in 2021.
Financial information was the most frequent target of such cyber attacks, according to the report. Cyber threats such as ransomware attacks against the industry have grown over the years amid challenges it already confronts: aging infrastructures and tight budgets.
The report, sponsored by Carahsoft, surveyed 167 professionals to assess the state of healthcare cybersecurity. Of those surveyed, 54% worked for healthcare provider organizations, 28% for consulting/vendor organizations, and 19% for other types of organizations. Most (61%) of those surveyed had primary responsibility for cybersecurity programs at their respective healthcare organization and 23% had some responsibility. Further, of those surveyed, 90% said they had a management role in healthcare cybersecurity.
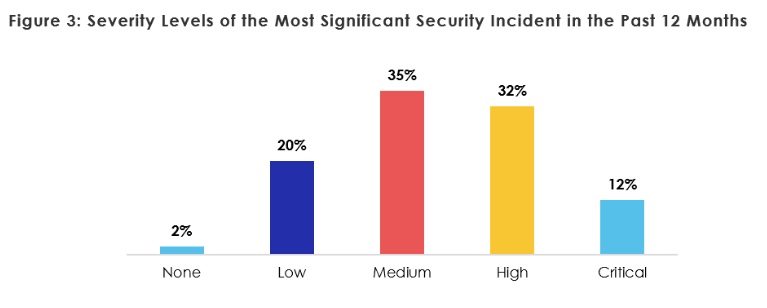
A substantial —67% — number of those who responded stated that in the past 12 months their healthcare organization combated significant security incidents, the report said. When considering how severe the security threat was that the organization faced, 12% considered it critical and 32% considered it a high threat.

A Deep-dive Into Specialty Pharma
A specialty drug is a class of prescription medications used to treat complex, chronic or rare medical conditions. Although this classification was originally intended to define the treatment of rare, also termed “orphan” diseases, affecting fewer than 200,000 people in the US, more recently, specialty drugs have emerged as the cornerstone of treatment for chronic and complex diseases such as cancer, autoimmune conditions, diabetes, hepatitis C, and HIV/AIDS.
Further, healthcare organizations said phishing attack were the first most common form of threat, accounting for 45% of security incidents. Ransomware attacks ranked second, comprising 17% of incidents. 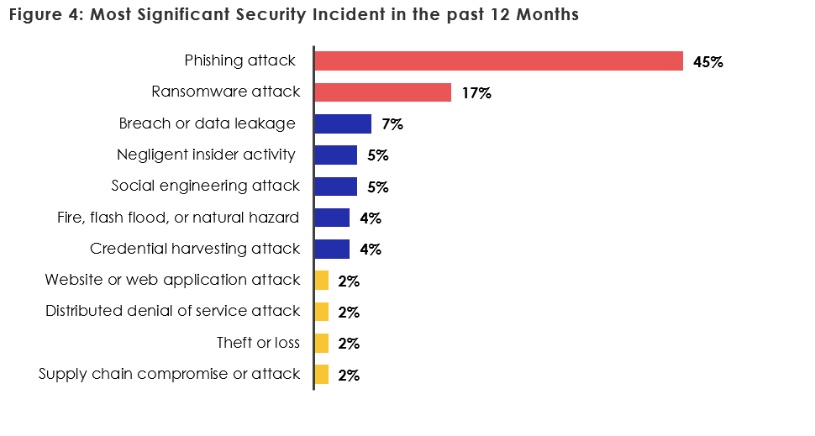
Additionally, phishing often played a major role in the security incidents. For example, 57% of those surveyed said the most significant security incident included phishing. Respondents indicated the percentage of each type of phishing that occurred: email phishing (71%), spear-phishing (67%), voice phishing/vishing (27%), whaling (27%), business e-mail compromise (23%), SMS phishing (21%), phishing websites (20%) and social media phishing (16%), according to the report.
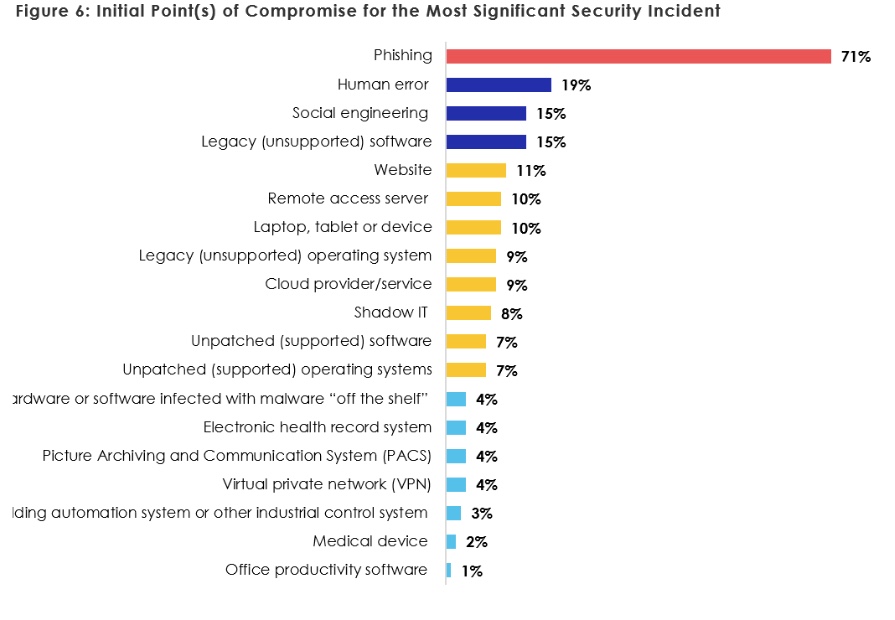
When exploring the initial point of contact that compromised cybersecurity, phishing was the most common, at 71%, the report said. Additionally, human error (19%) and social engineering (15%) as well as legacy software (15%) were the next most common initial points of compromise, according to the report.
As a result, the study recommended healthcare companies implement security awareness programs as well as insider threat detection and mitigation to improve security moving forward. Moreover, the report recommended upgrading software or replacing it altogether when needed.
As far as the target of the attacks, the 2021 report mirrored the findings of the 2020 HIMSS report, with 52% of the time financial information being the main target, followed by employee information (43%), and patient information (39%). Intellectual property only accounted for the target 15% of the time, the report said.
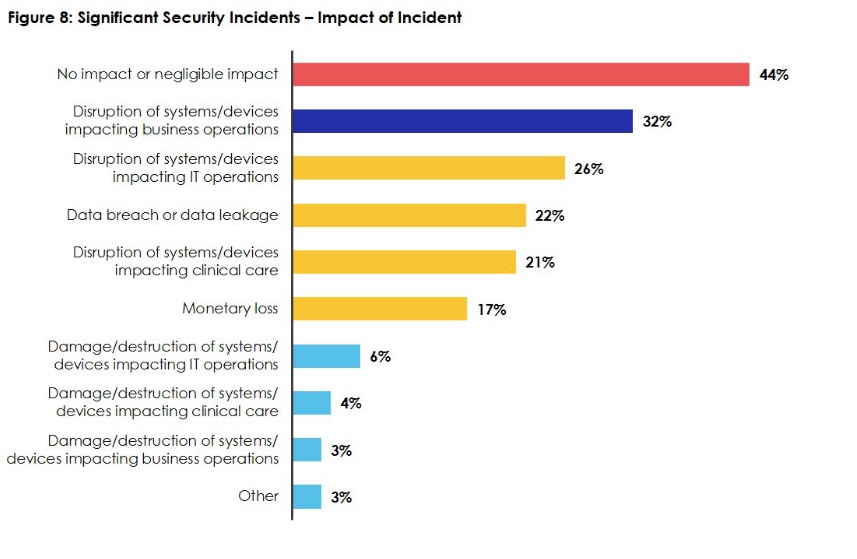
The attacks had a variety of impacts, ranging from data breaches and leakages to disruptions of systems/devices to monetary loss. However, 44% of the time the impact was nonexistent or negligible.
The study also looked at the cybersecurity budgets of healthcare companies. Despite 40% of companies only allocating 6% or less of their budgets to cybersecurity, 59% indicated an increase in their cybersecurity budget from 2020.
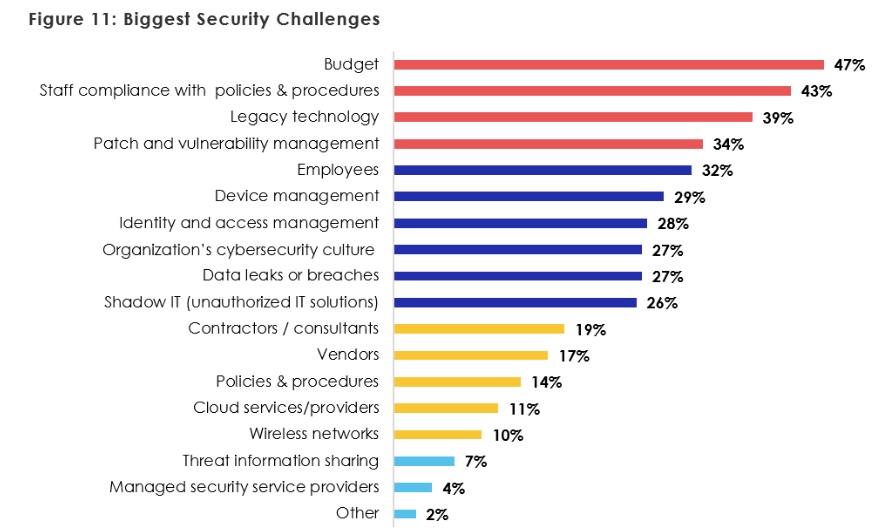
Additionally, budget, staff compliance with policies and procedures, legacy technology, as well as patch and vulnerability management were the top security challenges, according to the report.
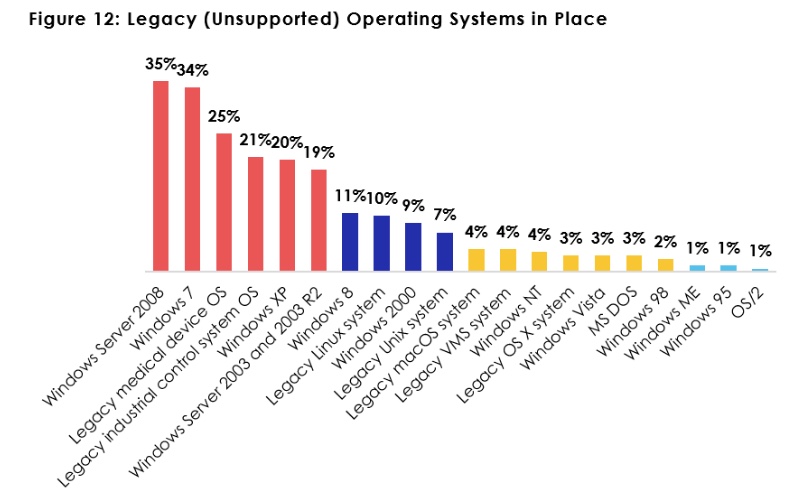
A vast majority at 73% said their healthcare organization had legacy operating systems. For example, 35% use Windows Server 2008 and 20% still use Windows XP. Shockingly, 19% use systems almost 20 years old: Windows Server 2003 and 2003 R2, the report found.
To remedy these vulnerabilities, healthcare organizations can implement a variety of security measures. The report recommends companies take inventory of their current risks and address weaknesses, prioritizing doing so in their budgets and training employees on safety measures. Not taking these actions would risk potential breaches moving forward.
Photo: WhataWin, Getty Images; Charts: HIMSS Healthcare












